In this otherwise illuminating post ‘Fixing Capitalism’s Oligopoly: A Response To Ray Dalio And John Mauldin‘ I noticed a particular aspect, which is the strong decrease of the number of publicly listed companies in favor of private capital.
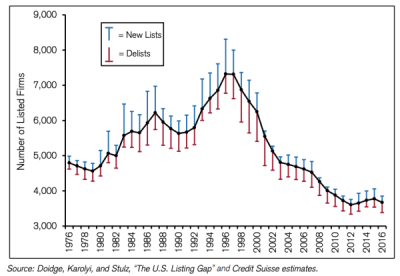
This trend is very noticeable since the end of the 1990’s. “The phenomenon is under-researched, but the papers that have been done look at issues like 1) impact of Sarbanes-Oxley (SOX), 2) growth of private equity capital, 3) the growth of M&A activity on Wall St and its need to keep the pipeline growing, and 4) a number of structural issues (like SOX) hurting small company formation“. The author believes that it is mostly the growth of private capital that explains this trend, which in turns tends to explain the much higher share of income captured by the wealthy (company owners). Another aspect is the increasing industry concentration with very large players that attain quasi monopolistic status.
This trend is at the same time interesting and problematic. It shows that probably a greater share of value creation is not directly accessible by the public through public shares. This, in turn, generates a number of interesting questions about the structure of our economy. Its agility is in question, and thus its future adaptability. Not quite the trend that would be expected in an increasingly unpredictable world.
